Have you ever wondered how intermittent fasting affects your cardiovascular health? It’s a hot topic in the health and wellness world right now, so let’s dive in and explore the impact of intermittent fasting on your heart health in more detail. In this article, you’ll learn about the latest research on the subject and discover how intermittent fasting can potentially improve your cardiovascular health.
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity in recent years, not only for its potential weight loss benefits but also for its impact on cardiovascular health. Research has shown that intermittent fasting can lead to improvements in various cardiovascular risk factors, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar control. By giving your body a break from constant eating and allowing it to enter a fasting state, intermittent fasting may promote cellular repair, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity, all of which contribute to a healthier heart.
In the next section, we’ll dig deeper into the specific ways in which intermittent fasting can positively affect your cardiovascular health. From its influence on oxidative stress and inflammation to its effects on lipid profiles and blood pressure, you’ll discover the scientific evidence behind the benefits of intermittent fasting on your heart health. So, if you’re curious to learn more about how intermittent fasting can potentially improve your cardiovascular health, keep reading!
Introduction
Intermittent fasting has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential health benefits. One area where it has shown promising results is in cardiovascular health. The health of our heart and blood vessels is crucial for overall well-being, and maintaining cardiovascular health can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and other related conditions. In this article, we will explore the impact of intermittent fasting on cardiovascular health and the mechanisms behind its effects.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a dietary pattern that cycles between periods of fasting and eating. It does not focus on what you eat but rather when you eat. There are several different types of intermittent fasting, including the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and restrict your eating window to 8 hours. Other approaches include alternate-day fasting, where you fast every other day, and the 5:2 diet, where you eat normally for five days and restrict calories on the other two.
Importance of Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health refers to the well-being of our heart and blood vessels. It plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and preventing various cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight, we can promote the optimal functioning of our cardiovascular system.
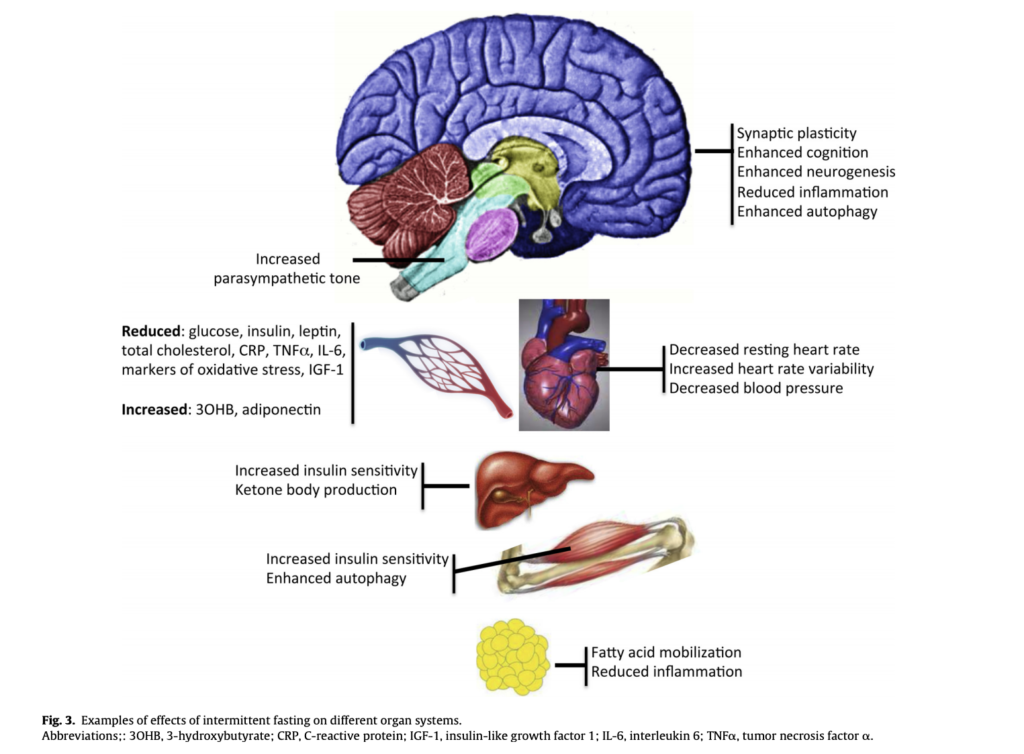
Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Cardiovascular Health
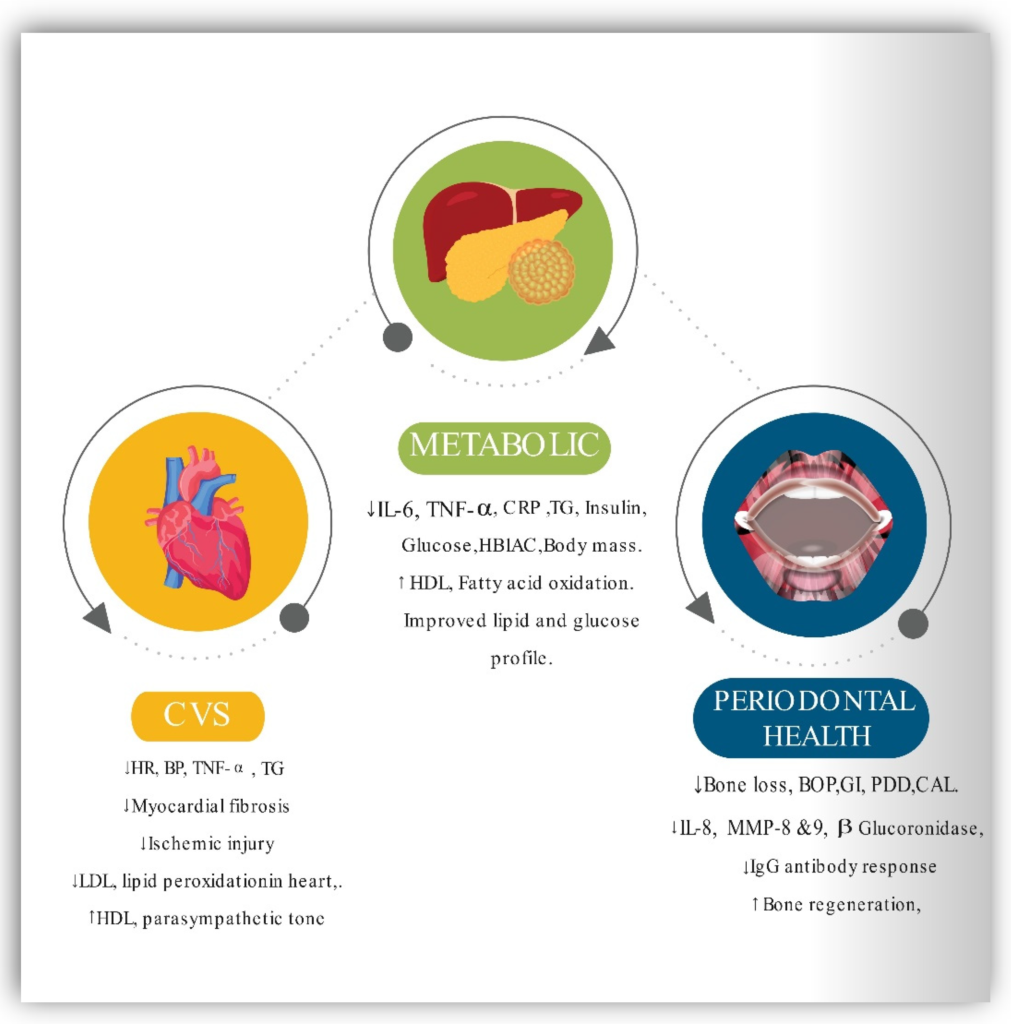
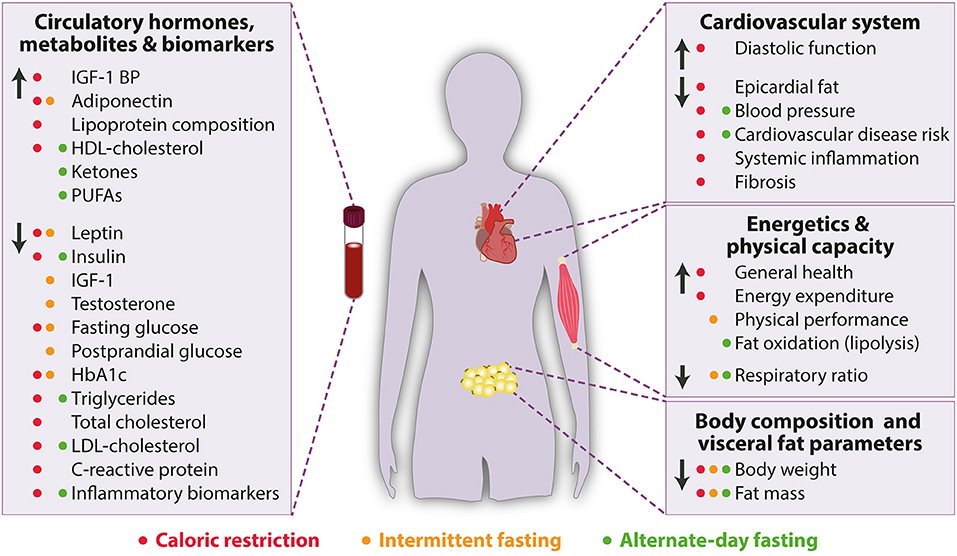
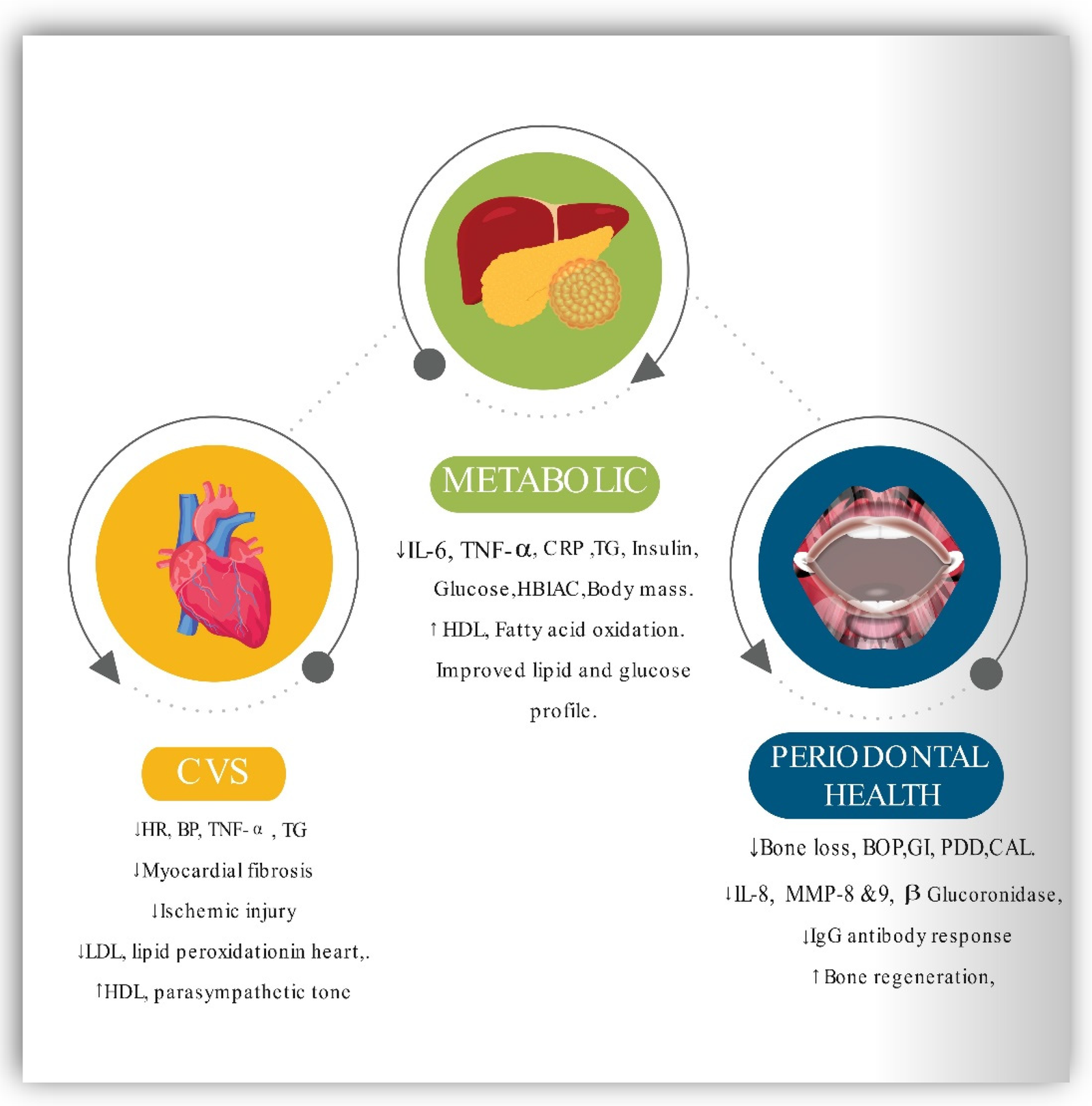
Several research studies have investigated the impact of intermittent fasting on cardiovascular health. The results have been quite promising, indicating that intermittent fasting can have positive effects on our heart and blood vessels. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that intermittent fasting led to reductions in blood pressure, total cholesterol levels, and triglycerides. These improvements in cardiovascular risk factors are likely to contribute to a lower risk of heart disease and related conditions.
However, it is important to note that there may be potential risks or drawbacks associated with intermittent fasting, specifically concerning cardiovascular health. Some studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may lead to a slight increase in LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) levels in some individuals. It is crucial to consider these factors and consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on an intermittent fasting regimen.
Mechanisms Behind the Impact
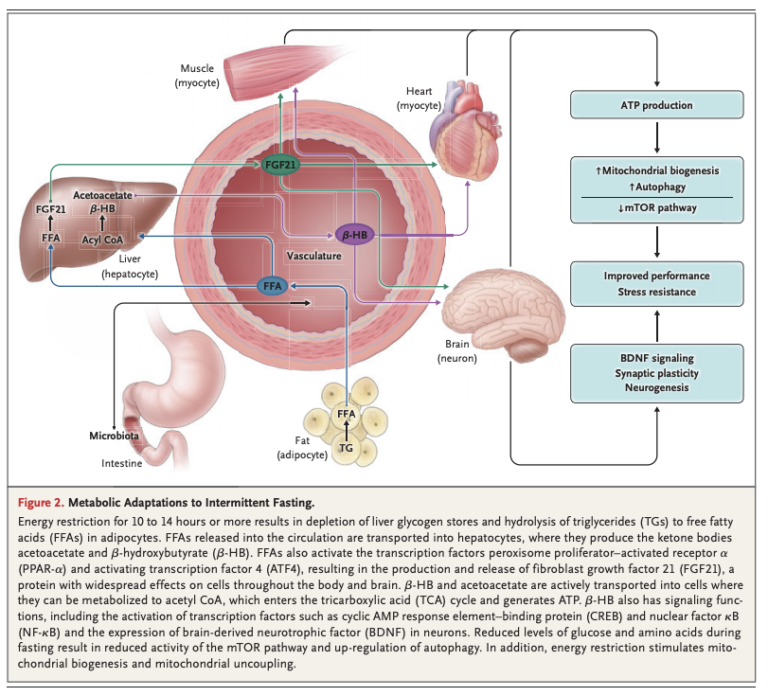
The precise physiological changes that occur during intermittent fasting and contribute to its impact on cardiovascular health are still being studied. However, researchers have identified several potential mechanisms that may explain the positive effects. One of the key factors is the influence of intermittent fasting on blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Fasting periods allow the body to regulate blood pressure and reduce cholesterol production, leading to improved cardiovascular health.
Additionally, intermittent fasting has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity. Insulin is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, and increased insulin sensitivity can help prevent insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, both of which are risk factors for heart disease. Furthermore, intermittent fasting has anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation markers in the body. Chronic inflammation is known to contribute to cardiovascular diseases, and by reducing inflammation, intermittent fasting may protect against heart disease.
Intermittent Fasting and Heart Disease
The connection between intermittent fasting and the prevention or treatment of heart disease is an area of active research. Various studies have shown that intermittent fasting can reduce the risk of heart disease by improving cardiovascular risk factors. For example, a study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that intermittent fasting resulted in lower blood pressure and improved blood lipid profiles, both of which are crucial for preventing heart disease.
In terms of managing existing heart conditions, intermittent fasting may also play a role. A study published in the Journal of Lipid Research suggested that intermittent fasting could help regulate lipid metabolism, specifically reducing LDL cholesterol levels, which are typically elevated in individuals with cardiovascular disease. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the extent of intermittent fasting’s impact on heart disease management.
Role of Intermittent Fasting in Weight Management
Weight management is closely linked to cardiovascular health, as maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of heart disease. Intermittent fasting has been found to be effective for weight loss and improving metabolic health. By restricting the eating window and reducing calorie intake, intermittent fasting can lead to a calorie deficit and promote fat loss. Additionally, it may help regulate hormones involved in appetite control, making it easier to adhere to a healthy eating pattern.
Other Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
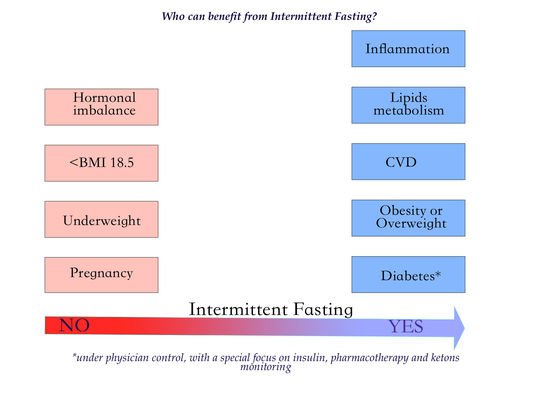
Apart from its impact on cardiovascular health, intermittent fasting has shown potential benefits in other areas as well. Research suggests that intermittent fasting can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, both of which are linked to various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, intermittent fasting has been found to improve blood lipid profiles by reducing triglyceride levels and increasing HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol).
It is worth noting that intermittent fasting may also help reduce other risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, such as blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and body mass index (BMI). However, further research is needed to fully understand the extent of these effects and their long-term consequences.
Choosing the Right Intermittent Fasting Approach
When considering intermittent fasting, it is important to choose an approach that suits your individual lifestyle and preferences. Factors such as work schedule, social commitments, and personal health conditions should be taken into consideration. It is also advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting an intermittent fasting plan, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns.
Conclusion
The impact of intermittent fasting on cardiovascular health is a subject of growing interest and research. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can have positive effects on cardiovascular risk factors, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and triglycerides. These improvements contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease and related conditions. However, it is crucial to consider potential risks and consult with healthcare professionals before embarking on intermittent fasting. Overall, intermittent fasting, when adopted under professional guidance, can potentially improve cardiovascular health and contribute to overall well-being.



Leave a Reply